Die Steel Improvements for AHSS Applications
- 2018-10-23 11:51:00
- LUQIMENG Original
- 1779
HITACHI Intro
− Steel Production Methods for Die & Tooling Steels
− Typical Failure modes of Die Steels for AHSS
− Solutions to improve Tooling Performances
−Steel Types, Coatings
− Hot Stamping Die Steels
− Pre Hardened Die Steels
− Grain Oriented Die Steel Study
Ask Your Tool Steel supplier……
• Test Certifications (actuals from Mill Source )
• Method of Manufacturing
• Forged, Rolled , etc.
• Recommended Heat Treat
Surface Coating advancements have greatly improved steel performances.
Part material
• Aluminum or Steel: What type & thickness?
• Press Size (Servo or Mechanical) & Strokes per minute cycle
• Current Die Construction
• Progressive or Transfer?
• Castings? Inserts?
• Tooling steels used ?
• What coating?
• Die Clearance
• Heat Treating Recipe
• Welding (In House? Outsource? Consumable used?)
• Failure Observations: What Happened?
• What's been tried so far?
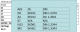
Coarse & directional carbide
• Large & anisotropic deformation after heat treatment
• Medium galling & wear resistance
• Characteristics will be affected by grain direction Small, dense & homogeneous carbide
• Small & isotropic deformation after heat treatment
• Same HT & Chem as D2
• Good galling & wear resistance
• Achieve higher hardness than
Machining of Pre-Hard Tool Steels @ 60 HRC
• 1) Machine Tool
• Rigid Construction:
• High Spindle Speed:20,000+
• 2) Cutting Tool
• Solid Carbide with ductile properties for interrupted cut
• 3) Consistent substrate of Die Steel
• Demands on Die Materials
−Wear
−Conductivity
−Watch for industry developments on 3D Additive Mfg. inserts w/ conformal cooling lines
• Use of higher alloyed Die Steel
• Upgrade to a NADCA Class C Hot Work Steel in place of AISI H13
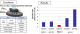
1. Conductivity
− Class B H13 is 32.6 @ 600C Class C is 35.8 @ 600C
− Better for heat conductivity than H13 means better cycle times .
2. Toughness:
− Why? Higher Impact Values (charpy) prevent cracking on the surface of Hot Stamping Dies close to the cooling channel .
3. Wear:
− Why? NADCA Class C ( HITACHI DAC-MAGIC ) is higher strength under high temperature. Diesurfaces can reach ~ 400C & higher alloyed steels are needed to extend wear.
4. Coatablity
− Coatable and Wear resistance at room temperature, almost same as H13.
• Review Die Standards & allow for areas requiring better tooling steels in trouble-spots
• Compare results with other steels in side by side like- environments
• Insist on controlled HT path & Welding steps
• Ask for grain orientation on larger cross sections
• “If you can’t use a better tool steel, use your tool steel better”